Service discovery - Setting up the targets
Our service discovery integration using file based discovery will need a file to watch, which
will be a
targets.yml file that needs to be located in the same Prometheus
instance directory holding your workshop-prometheus.yml file. Edit this
target file to look like this (note for container installs we are using a podman variable, if
using source install then replace all configuration targets with
localhost:PORT_NUMBER):
- targets: ["host.containers.internal:11111"]
- targets: ["host.containers.internal:22222"]
labels:
job: "services"
env: "production 2"
- targets: ["host.containers.internal:44444"]
labels:
job: "services"
env: "development"
Intermezzo - A word about Prometheus setup
The next step is configuring a Prometheus instance to make use of the file based discovery
targeting our newly created
Now let's get to work on that configuration...
targets.yml file. If you have been following the
previous workshop labs, you most likely have a heavily configured
workshop-prometheus.yml file. In the next slide you'll see the minimum
setup you'll use for the rest of this lab. To achieve the same configuration, it's handy if you
just comment out any unused or unneeded parts of the configuration by commenting out lines using
# (hash mark or pound sign).Now let's get to work on that configuration...
Service discovery - Configuring file base discovery
Now we need to adjust the configuration of our Prometheus instance to use file based discovery
and watch the newly created
targets.yml file. To do that ensure the
workshop-prometheus.yml file contains the following (note the different
files location based on container image or source binary usage):
# workshop config
global:
scrape_interval: 5s
scrape_configs:
# Scraping Prometheus.
- job_name: "prometheus"
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090"]
# File based discovery.
- job_name: "file-sd-workshop"
file_sd_configs:
- files:
- "/tmp/targets.yml" <<<< if using src binary, replace with: "- targets.yml"
Service discovery - Adding targets to buildfile
Before you rebuild the container image, noting that we don't have to add the newly created
targets.yml file to the buildfile. This file is hosted externally to the
static configuration so we can dynamically update it. Rebuild the container image using the
following Buildfile:
FROM prom/prometheus:v3.0.1
ADD workshop-prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus
Service discovery - Building a container image
Now you can build your own container image with our custom configuration inserted:
$ podman build -t workshop-prometheus:v3.0 -f Buildfile
STEP 1/2: FROM prom/prometheus:v3.0.1
Resolving "prom/prometheus" using unqualified-search registries
Trying to pull docker.io/prom/prometheus:v3.0.1...
Getting image source signatures
Copying blob sha256:bd0d00e6784783d31bbe04e7b3bf2f54478ed0c46afc05a63e4a0f1f72076f03
Copying blob sha256:d2f8aae8d80e67a268ee5a3a7c47544bf2cdd7f9c177bd3e9a3d0b2cc100f00b
Copying blob sha256:fcd10bff2ba698a61831db119b3e42b946a2007e735a1c2368233950ac183c44
Copying config sha256:57847a717fc6727452cd1ed5b02200e3030aba04ca13cbdc536ee99402643440
Writing manifest to image destination
STEP 2/2: ADD workshop-prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus
--> Using cache a5e118ee2fb880b55d6b189dc6189837dd0ba73bb0f97e3b67a22eb672d1b776
COMMIT workshop-prometheus:v3.0
--> a5e118ee2fb8
Successfully tagged localhost/workshop-prometheus:v3.0
a5e118ee2fb880b55d6b189dc6189837dd0ba73bb0f97e3b67a22eb672d1b776
Service discovery - Starting Prometheus instance
To start Prometheus is depending on whether you've chosen to install from the source binary, or
run it in an open source container. Start Prometheus using a command below that matches your
choice:
# Start Prometheus using source.
#
$ ./prometheus --config.file=workshop-prometheus.yml
# Start Prometheus in a container, mounting current directory to the container /tmp directory.
#
$ podman run -p 9090:9090 -v ./:/tmp workshop-prometheus:v3.0 --config.file=/etc/prometheus/workshop-prometheus.yml
Service discovery - Validating file based discovery
After starting Prometheus, validate the scraping is working through the file based discovery by
opening the console at
http://localhost:9090 and selecting from the menu
STATUS -> TARGETS and finding the two production and one development
service environments grouped under file-sd-workshop:

Service discovery - Validating using PromQL
You can also validate that the three services environments are being scraped by using a PromQL
query
UP{job="services"} as follows:

But wait, why are there only two services listed? If you looked closely at the targets we
configured, the production 1 environment has no labels defined, so it's just using generated
labels, let's fix that and watch Prometheus auto-discover them.
Service discovery - Updating targets for discovery
Update the
targets.yml file, adding job and
env labels and have our Prometheus instance discover them dynamically. Note
when using container images it takes a certain amount of time for Prometheus to check for those
new changes:
- targets: ["host.containers.internal:11111"]
labels:
job: "services"
env: "production 1"
- targets: ["host.containers.internal:2222"]
labels:
job: "services"
env: "production 2"
- targets: ["host.containers.internal:44444"]
labels:
job: "services"
env: "development"
Service discovery - Validating auto-discovery
After a period of time, you'll see the three service environments are being scraped by using a
PromQL query
UP{job="services"} as follows:
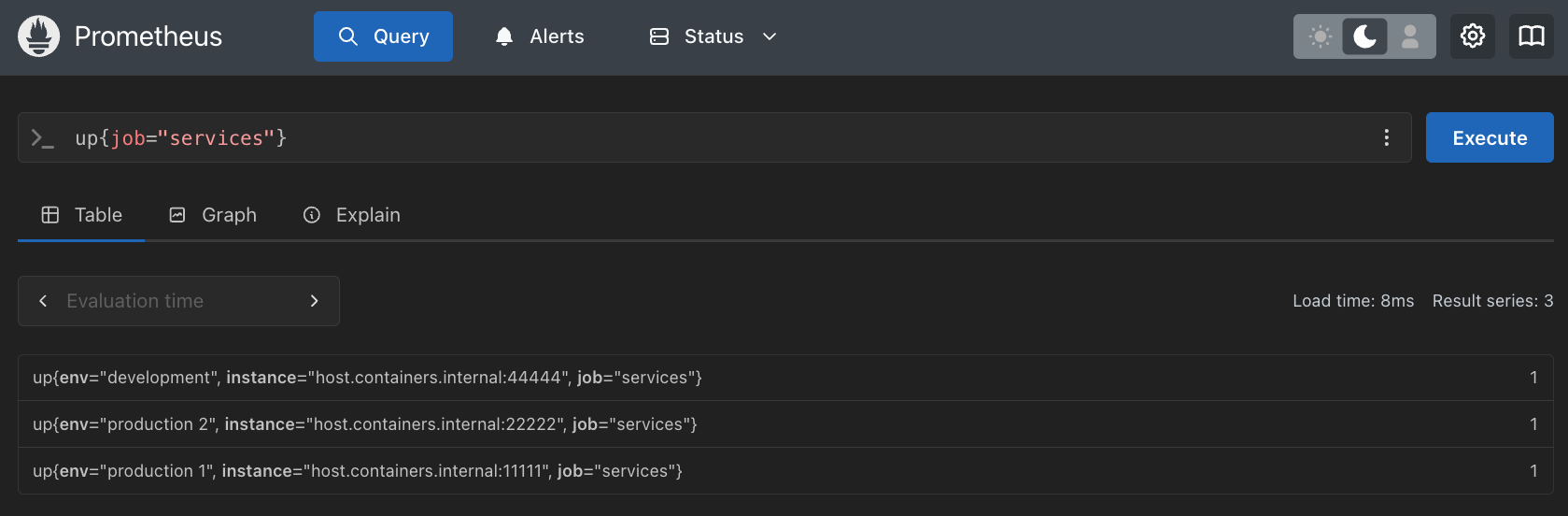
Service discovery - Updating staging for discovery
Now we can update our
targets.yml file and have our Prometheus instance
discovering those changes dynamically. Let's promote our development services infrastructure to
STAGING by updating the env label:
- targets:
- "host.containers.internal:11111"
labels:
job: "services"
env: "production 1"
- "host.containers.internal:22222"
labels:
job: "services"
env: "production 2"
- targets:
- "host.containers.internal:44444"
labels:
job: "services"
env: "staging"
Service discovery - Validating staging updates
After saving the
targets.yml file changes, you can query the services
targets using the same methods shown earlier (here with PromQL) to verify Prometheus picked
up the changes dynamically:

Service discovery - Individual exercise
Before you complete this lab, a final exercise to apply all you have learned.
Start a new instance of your services infrastructure and run it on an unused port on your machine (localhost:33333 for example).
Add this new infrastructure target, give it a job label, and name the environment testing.
Start a new instance of your services infrastructure and run it on an unused port on your machine (localhost:33333 for example).
Add this new infrastructure target, give it a job label, and name the environment testing.
Service discovery - Validating testing updates
Verify the discovery is collecting testing metrics by querying the services targets using the same
methods shown earlier (here with PromQL):

Lab completed - Results

Next up, metrics monitoring at scale...

Contact - are there any questions?
Eric D. Schabell
Director Evangelism
Contact: @ericschabell {@fosstodon.org) or https://www.schabell.org
Director Evangelism
Contact: @ericschabell {@fosstodon.org) or https://www.schabell.org
Up next in workshop...
Service discovery - Setting up the targets Our service discovery integration using file based discovery will need a file to watch, which
will be a targets.yml file that needs to be located in the same Prometheus
instance directory holding your workshop-prometheus.yml file. Edit this
target file to look like this (note for container installs we are using a podman variable, if
using source install then replace all configuration targets with localhost:PORT_NUMBER ): - target s: [ "host.containers.internal:11111" ]
- target s: [ "host.containers.internal:22222" ]
label s: jo b: "services" en v: "production 2" - target s: [ "host.containers.internal:44444" ]
label s: jo b: "services" en v: "development"